|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
- 1. Notes on choosing a switching
power supply?
Ans:
-
To increase the reliability of the S.P.S., we suggest users
choose a unit that has a rating of 30% more power than actual need. For
example, if the system needs a 100W source, we suggest that users choose a
S.P.S. with 130W of output power or more. By doing this, you can effectively
boost the reliability of the S.P.S. in your system.
-
We also need to consider about ambient temperature of the
S.P.S. and whether there is additional device for dissipating the heat. If the
S.P.S. is working in a high temperature environment, we need to make some
derating to the output power. The derating curve of "ambient temperature"
versus "output power" can be found on our spec sheets.
-
Choosing functions based on your application:
-
Protection function: Over Voltage Protection (OVP), Over
Temperature Protection (OVP), Over Load Protection (OLP), and etc.
-
Application function: Signaling Function (Power Good, Power
Fail), Remote Control, Remote Sensing, and etc.
-
Special function: Power Factor Correction (PFC),
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) function.
-
Make sure that the model qualifies for the safety standards
and EMC regulations you need.
- 2. How do we choose a power
supply to charge a battery?
Ans:
-
MEAN WELL has ESC, SC, PA, PB series for battery charger
purpose (120~360W). If these series does not meet customers' demands and they
like to choose a power supply as a charger, we advice to pick up one which over
load protection (OLP) mode is constant current limiting. The models in this
mode provide constant current even when the protection circuit is triggered.
The second choice is fold-back current limiting or constant wattage
model. In this model, when a battery is running low, the output current of the
power supply will gently increase. The level of increase depends on battery's
capacity and degree of exhaustion.
Hiccup or shut down model are not
recommended because it will stop to generate current when OLP happens.
- 3. Can MEAN WELL's power supply
be used in the range of 45Hz ~ 440Hz? If YES, what will happen?
Ans:
-
MEAN WELL's power supply can be used within this frequency
range. But if the frequency is too low, the efficiency will also be
lower. For example, when a SP-200-24 is operated under 230VAC and rated load,
if the frequency of AC input is 60 Hz, the efficiency is around 84%; however,
if the frequency of AC input reduces to 50 Hz, the efficiency will be around
83.8%. If the frequency is too high, the power factor of the S.P.S. with PFC
(power factor correction) function will reduce and this also will cause higher
leakage current. For example, when a SP-200-24 is operated under 230VAC and
rated load, if the frequency of AC input is 60 Hz, the power factor is 0.93 and
the leakage current is around 0.7mA; however, if the frequency of AC input
increase to 440 Hz, the power factor will decrease to 0.75 and the leakage
current will rise to around 4.3mA.
- 4. If we need a 24V output power
supply, but MEANWELL does not have this model, can we use two 12V power
supplies connecting in series instead of one 24V power supply?
Ans:
-
YES, basically you can do this to get the right output
voltage, but be careful that the rated output current of the series system
should be the rating of the minimum one in these series connected power
supplies. Furthermore, we like you to parallel a diode at the output of power
supply to prevent possible damage of internal capacitors.
- 5. If we need a 600W output, can
we use two units of S-320 connected in parallel?
Ans:
-
No, you can not do this connection because S-320 is not
equipped with the parallel function. When two power supplies are connected in
parallel, the one with higher output voltage will share more loading and
deliver more (even "all") power to the load and cause these two power supplies
to be unbalanced. We suggest using PSP-300 or PSP-500 because it is equipped
with the current sharing function.
- 6. When testing a dual output
power supply, the +5V channel is correct, but the +12V channel is over the
specification. What is going on?
Ans:
-
There are some minimum-load requirements on MEAN WELL's
multi-output power supplies, please refer to the specification first before
connecting the load. When the load condition is 5V/4A, 12V/0A, the output
voltage of the 12V channel will be around 12.8V that is over the ±6% of voltage
deviation (12.72V) specified in the spec. sheet. If we add in the minimum load
0.2A to the 12V channel, the 12V channel will reduce to around 12.3V which is
within the specification.
- 7. Why I can not turn on the
power supply smoothly when the loads are motors, light bulbs or capacitive
loads?
Ans:
-
If you connect the S.P.S. to motors, light bulbs, or high
capacitive loads, you will have a high output surge current when you turn on
the S.P.S. and this high surge current will cause failure of start up. We
suggest using S.P.S. with constant current limiting protection to deal with
these loads.
- 8. Why did the power supply shuts
down during operation and after turning it off, I can restart the power supply
again?
Ans:
-
In general there are two circumstances that will cause the
power supply to shut down. The first one is the activation of the
over-load-protection (OLP). To deal with this situation, we suggest increasing
the rating of the output power or modifying the OLP point. The second one is
the activation of over-temperature protection (OTP) when the internal
temperature reaches the pre-set value. All of these conditions will let the
S.P.S. enter protection mode and shut down. After these conditions are removed,
the S.P.S. will be back to normal.
- 9. The output ground (GND) and
frame ground (FG) is the same point in my system, can MEAN WELL's power
supplies be used in such system?
Ans:
-
Yes. Since our products are designed based on isolation
concept, it will be no problem that the output ground (GND) and frame ground
(FG) is the same point in your system. But, EMI may be affect by this
connection.
- 10. During the operation of MEAN
WELL power supply, there is some leakage current on the case. Is this normal?
Will this leakage current hurt human body?
Ans:
-
Due to the requirement of EMI, there will be some Y capacitors
between line and neutral to the FG (case) to improve EMC. These Y capacitors
will cause some leakage current flow from line or neutral to the case (normally
case will be connected to earth ground). For example, IEC-60950-1 requires that
this current should be less than 3.5mA for IT equipment, so basically the
leakage current you find on the case will not hurt human body. Proper
connection to Earth ground will solve the leakage current problem.
- 11. For certain need, is it
possible to reduce the noise of fan?
Ans:
-
Noise is directly related to the fan which is build into the
power supply. Lowering the airflow of the fan means reducing the heat
dissipation ability. It will also influence the reliability of the products.
Furthermore, minimum airflow of fans is defined by Safety Organization and a
safety appendage will be needed if using a new fan. Generally, when we choose a
suitable power supply, fan is not necessary if wattage is under 150W. Between
150~500W, both fan and fanless products are available. Above 500W, a fan is
needed.
- 12. What should be noticed when
installing a power supply in vertical and horizontal directions?
Ans:
-
Most small wattage and fanless power supplies are mainly
installed in the horizontal position. If you have to install it vertically
because of mechanical limitation, you should consider the output derating due
to the heat concern. The temperature derating curve can be found on the spec
sheet. Regarding the power supplies with built-in fan or the application has
forced cooling system, vertical and horizontal installations have less
difference.
Ex. In SP-150 derating curve, the ambient temperature difference in
application is 5 Celsius from vertical to horizontal. The output wattage in
forced cooling can be 20% higher than air cooling convection.
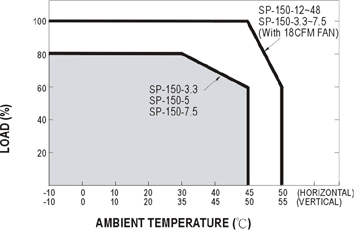
- 13. Why the fan is not running
after turning on certain models?
Ans:
-
Some models control the fan based on internal temperature to
extend its life time. For example, the Fan ON temperature for the S-240 series
is ≧ 40C (RT1). If the internal temperature does not reach the preset value,
the fan will remain still until receiving the start up signal.
- 14. What is "Inrush Current"?
What will we notice?
Ans:
-
At input side, there will be (1/2 ~1 cycle, ex. 1/120 ~ 1/60
seconds for 60 Hz AC source) large pulse current (20~60A based on the design of
S.P.S.) at the moment of power on and then back to normal rating. This "Inrush
Current" will appear every time you turn on the power. Although it will not
damage the power supply, we suggest not turning the power supply ON/OFF very
quickly within a short time. Besides, if there are several power supplies
turning on at the same time, the dispatching system of AC source may shut off
and go into protection mode because of the huge inrush current. It is suggested
that these power supplies start up one by one or use the remote control
function of S.P.S. to turn them on/off.
- 15. What is PFC?
Ans:
-
PFC stands for Power Factor Correction. The purpose of PFC is
to improve the ratio of apparent power and real power. The power factor is only
0.4~0.6 in non-PFC models. In PFC models, the power factor can reach above
0.95. The calculation formulas are as below:
Apparent Power=Input Voltage x
Input Current (VA)
Real Power= Input Voltage x Input Current x Power Factor (W)
From the environment friendly point, the electric power plant needs to generate
a power which is higher than apparent power in order to steadily provide
electricity to the market. The real usage of electricity should be defined by
real power. Assuming the power factor is 0.5, the power plant needs to produce
more than 2VA to satisfy 1W real power. On the contrary, if the power factor is
0.95, the power plant only needs to generate more than 1.06VA to provide 1W
real power need. It will be more effective.
- 16. What is the difference
between -V and COM which are marked on the output side?
Ans:
-
COM (COMMON) means common ground. Please see below:
Single
output: Positive pole (+V), Negative pole (-V)
Multiple output (Common ground):
Positive pole (+V1, +V2,.), Negative pole (COM)
- 17. In MEAN WELL's catalog, we
see AC and DC at input, what is it all about?
Ans:
-
Due to different circuit designs, MEAN WELL power supply's
input consists of three types as below:(√2VAC≒VDC)
a.85~264VAC;120~370VDC
b.176~264VAC;250~370VDC
c.85~132VAC/176~264VAC by Switch; 250~370VDC
- In a
and b inputs models, power supply can work properly no matter under AC or DC
input. Some models need correct connection of input poles, positive pole
connects to AC/L; negative pole connects to AC/N. Others may require opposite
connection, positive pole to AC/N; negative pole to AC/L. If customers make a
wrong connection, the power supply will not be broken. You can just reverse the
input poles and power supply will still work.
- In c input models, please
make sure that you switch the 115/230V input correctly. If the switch is on the
115V side and the real input is 230V, the power supply will be damaged.
- 18. Why the input voltage marked
on the spec. sheet is 88~264 VAC while the label on the power supply says that
it is 100~240VAC?
Ans:
-
During safety verification process, the agency will use a
stricter standard -- ±10%(IEC60950 uses +6%, -10%) of the input voltage range
labeled on the power supply to conduct the test. So, operating at the wider
input voltage range as specified on the spec. sheet should be fine. The
narrower range of input voltage labeled on the power supply is to fulfill the
test standard of safety regulation and make sure that users insert input
voltage correctly.
- 19. Will MeanWell's products with
CE marking meet the EMC requirements after assembling into my system?
Ans:
-
We cannot guarantee 100% that the final system can still meet
the EMC requirements. The location, wiring and grounding of the switching power
supply in the system may influence its EMC characteristics. In different
environment or applications, the same switching power supply may have different
outcomes. Our test results are based on setup shown in the EMC report.
- 20. What is different between
information (EN60950-1) and medical (EN60601-1) safety standard?
Ans:
-
According to safety standard, the leakage current in EN60950-1
Class I cannot exceed 3.5mA; in EN60601-1 cannot exceed 0.3mA. Others criteria
like safe distance and numbers of fuse are also different. Please consult the
diagram below:

- 21. What is MTBF? Is it distinct
from Life Cycle?
Ans:
-
MTBF and Life Cycle are both indicators of reliability. MEAN
WELL uses MIL-HDBK-217F as the core of MTBF. An expected reliability is
forecasted through accounting component's number (exclude fans). The exact
meaning of MTBF is after continuously using of power supply in a certain time,
the probability of operating properly is 36.8%(e-1=0.368). If power supply is
continuously used at double the MTBF time, the probability of operating
properly becomes 13.5%(e-2=0.135).
Life Cycle is found through using the
temperature rise of electrolytic capacitor to estimate the approximate life of
power supply. For example, SP-750-12 MTBF=769.3K hours; electrolytic capacitor
C108 Life Cycle=202.2K hours (Ta=45° C).
|

|

|
|
|